Plastic Injection Mold
Plastic Injection Molds are the main tools for creating plastic parts. They are the most widely used mold category in the plastics industry to produce parts ranging from small to large series.
Plastic injection molds share various common elements and characteristics:
- Cavity and Core: These are the main parts of the mold that define the shape of the plastic part to be produced. The cavity forms the outer surface of the part, while the core forms the internal details.
- Injection Channels: These are the passages through which the molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity. They must be designed to ensure uniform material distribution and avoid filling defects.
- Ejectors: These are mold components that allow the plastic part to be ejected from the mold once the injection process is complete. They can be mechanically or hydraulically activated.
- Cooling Systems: They are used to control the mold’s temperature during the injection process. Cooling channels are integrated into the mold to dissipate heat and ensure uniform cooling of the part.
- Ventilation Systems: They are used to evacuate gases or trapped air in the mold during the injection process to avoid air bubbles or surface imperfections on the plastic part.
Working principle of a Plastic Injection Mold:
Injection:
The plastic, in the form of pellets, is heated and melted in the heated barrel of the injection press. Once melted, the plastic is pushed by a screw through the injection nozzle and injected under high pressure into the mold cavity.
Cooling:
Once the plastic is injected into the mold, the cooling process begins. The integrated cooling channels in the mold dissipate the heat, allowing the plastic to harden and take the cavity shape.
Ejection:
Once the plastic has sufficiently cooled and hardened, the ejectors are activated to eject the plastic part from the mold. The part is then retrieved, and the mold is ready for a new injection cycle
Bi-Material Injection


Bi-Material Plastic Injection, also known as bi-injection, is an advanced technique used in the manufacture of plastic parts. It involves two successive molding stages, each using a different thermoplastic material. This approach allows creating complex parts with specific characteristics to meet various aesthetic and functional needs.
This method is commonly used to produce parts with features such as:
- Contrasting color combinations or distinct colored areas.
- Varied material compositions with, for example, rigid and flexible zones or the use of technical and aesthetic materials.
- Special functionalities like a "grip" effect for better adhesion or a "soft" touch for increased comfort.

In addition to meeting these design requirements, bi-material injection also offers practical advantages. For example, it allows the direct integration of sealing functions in the part, avoiding the need for additional assemblies and improving manufacturing efficiency.
To implement this technique, several types of molds are used:
- Transfer Molds: The part is moved manually or by a robotic system in the same mold for the second injection.
- Rotary Plate Molds: The mold’s movable part rotates 180 degrees to place the first molding in the second material’s cavity, facilitating the process.
- Rotary Base Molds: The rotation mechanism is integrated into the mold itself, allowing the movable cavity to pivot before returning to its original position.
- Gate or Slideback Molds: A core movement creates the necessary space for the second injection.
These different approaches offer great flexibility and precision, allowing the production of sophisticated bi-material parts to meet the most complex industrial application requirements.
Curious to learn more about bi-material injection molding? Learn more
Gas-assisted injection
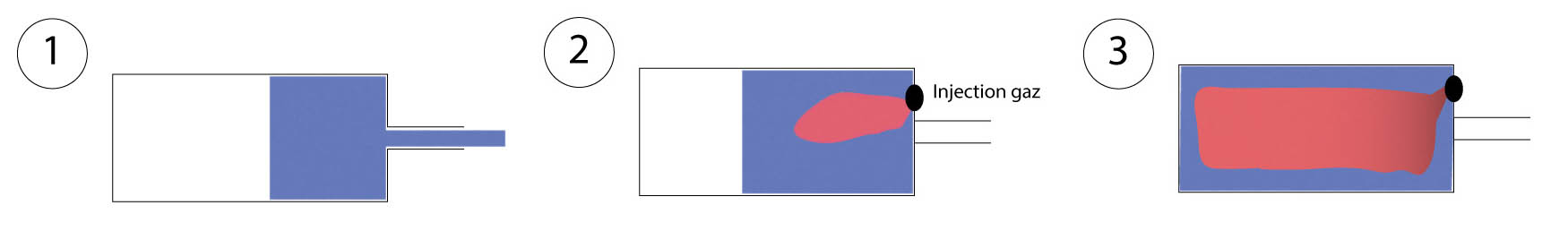
A gas-assisted injection mold, is a device specifically designed for the plastic injection process to optimize mold cavity filling and improve the quality of molded parts. The gas-assisted mold is typically made from high-quality hardened steel to ensure its durability and resistance to heat and pressure.
Working principle:
- Before the plastic injection process begins, the integrated channels in the mold are supplied with high-pressure nitrogen gas.
- When the molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity, the circulating nitrogen gas acts as a gas cushion, pushing the molten plastic towards the mold cavity's furthest areas.
- This allows for a more uniform filling of the mold cavity, thus reducing the risks of molding defects such as weld marks, flow lines, or air voids.
Advantages:
- Lighten plastic parts (up to 40%)
- Mechanically strengthen by removing ribs and placing gas veins judiciously
- Ensure controlled shrinkage and stresses, maintaining dimensional stability
- Allow for different designs with varying thicknesses
Eliminate sink marks and improve surface states with controlled weld lines - Reduce closing forces
- Shorten cycle times

Curious to learn more about gas-assisted injection molding? Learn more
Compression Mold
NOCENTE has extensive technical expertise in compression molds used for the production of parts made from composite materials, rubber, or silicone. The material is placed into the mold cavity before being compressed under pressure.
Learn moreThermoset Injection Mold
Thermoset injection is a manufacturing process used to transform thermosetting materials into finished parts. Unlike thermoplastics, thermosetting materials cure irreversibly when exposed to heat and pressure, forming robust chemical bonds.
Learn more